This material is intended for people without medical education who want to know more about osteochondrosis than what is written in popular publications and on the websites of private clinics. Patients ask doctors of various specialties questions that characterize a complete misunderstanding of the topic of osteochondrosis. Examples of such questions include: "Why does my osteochondrosis hurt? "», "congenital osteochondrosis has been discovered, what should I do? Perhaps the apotheosis of such illiteracy can be considered a fairly common question: "Doctor, I have the first signs of chondrosis, how scary is it? This article aims to structure the material about osteochondrosis, its causes, manifestations, methods of diagnosis, treatment and prevention, and to answer the most frequently asked questions. Since we are all, without exception, patients with osteochondrosis, this article will be useful to everyone.
What is osteochondrosis?
The name of the disease is scary when it is not clear. The medical suffix "-oz" means proliferation or hypertrophy of certain tissues: hyalinosis, fibrosis. An example would be liver cirrhosis, when the connective tissue grows and the functional tissue, the hepatocytes, decreases in volume. There may be a buildup of pathological proteins, or amyloids, that should not normally be present. This storage disease will then be called amyloidosis. There may be significant enlargement of the liver due to fatty degeneration, called fatty hepatosis.
Well, it turns out that with intervertebral osteochondrosis, the cartilaginous tissue of the intervertebral discs increases in volume, because "chondros, χόνδρο" translated from Greek into Russian means "cartilage"? No, chondrosis, or more precisely osteochondrosis, is not a storage disease. In this case, no real growth of cartilage tissue occurs; we are simply talking about a change in the configuration of the intervertebral cartilaginous discs under the influence of many years of physical activity, and we considered above what happens in each individual disc. The term "osteochondrosis" was introduced into the clinical literature by A. Hilderbrandt in 1933.
How do the biomechanics of a dehydrated disc change its shape? Due to excessive load, their outer edges swell, rupture and protrusions are formed, then intervertebral hernias or cartilaginous nodes that protrude beyond the normal contour of the disc. This is why chondrosis is called chondrosis, because cartilaginous lymph nodes - herniations - appear where cartilage should not be, behind the outer contour of a healthy disc.
The edges of the vertebrae, adjacent to the disc, also hypertrophy, forming coracoids, or osteophytes. Therefore, such a mutual violation of the configuration of cartilage and bone tissue is collectively called osteochondrosis.
Osteochondrosis refers to dystrophic-degenerative processes and is part of normal, normal aging of intervertebral discs. None of us is surprised that the face of a 20-year-old girl looks slightly different from her face at 70, but for some reason everyone believes that the spine, its intervertebral discs, do notdo not undergo the same pronounced temporary phenomenon. changes. Dystrophy is a nutritional disorder and degeneration is a violation of the structure of the intervertebral discs that follows a long period of dystrophy.
Causes of osteochondrosis and its complications
The main cause of simple physiological osteochondrosis can be considered the way a person moves: walking upright. Man is the only species on earth that walks on two legs among all mammals, and this is the only means of locomotion. Osteochondrosis has become the scourge of humanity, but we have freed our hands and created civilization. Thanks to standing walking (and osteochondrosis), we not only created the wheel, the alphabet and mastered fire, but you can also sit in the warmth of your home and read this article on your computer screen.
The closest relatives of man, higher primates - chimpanzees and gorillas, sometimes get up on two legs, but this method of movement is auxiliary to them and most often they still move on four legs. In order for osteochondrosis to disappear, just like intensive aging of the intervertebral discs, a person needs to change the way they move and remove the constant vertical load on the spine. Dolphins, killer whales and whales do not suffer from osteochondrosis, and dogs, cows and tigers do not suffer from it. Their spine does not support long-term static and shock vertical loads, since it is in a horizontal state. If humanity goes to sea, like Ichthyander, and the natural way of movement is scuba diving, then osteochondrosis will be defeated.
The upright posture has forced the human musculoskeletal system to evolve in the direction of protecting the skull and brain from shock loads. But discs – elastic pads between the vertebrae – are not the only method of protection. A person has an elastic arch, cartilage of the knee joints, physiological curves of the spine: two lordoses and two kyphoses. All this allows you not to "shake" your brain even while running.
Risk factors
But doctors are interested in risk factors that can be modified and avoid complications of osteochondrosis, which cause pain, discomfort, limited mobility and reduced quality of life. Let's come back to these risk factors, so often ignored by doctors, particularly in private medical centers. After all, it is much more profitable to constantly treat a person than to point out the cause of the problem, solve it and lose the patient. Here they are:
- the presence of longitudinal and transverse flat feet. Flat feet prevent the arch from bouncing and the shock is transmitted upward to the spine without softening. The intervertebral discs experience significant stress and collapse quickly;
- overweight and obesity – requires no comment;
- improper lifting and carrying of heavy objects, with uneven pressure on the intervertebral discs. For example, if you lift and carry a sack of potatoes on one shoulder, the intense load will fall on one edge of the discs, and it may be excessive;
- physical inactivity and a sedentary lifestyle. It was said above that it is in a sitting position that the maximum pressure on the discs occurs, since a person never sits straight, but always leans "slightly";
- chronic injuries, slipping on ice, intense weightlifting, contact martial arts, heavy hats, banging your head on low ceilings, heavy clothing, carrying heavy bags in your hands.
The risk factors that can affect each person have been listed above. We deliberately do not list diseases here - connective tissue dysplasia, scoliotic deformity, which changes the biomechanics of movement, Perthes disease and other conditions that aggravate and aggravate the course of physiological osteochondrosis and lead to complications. These patients are treated by an orthopedist. What are the common symptoms of complicated osteochondrosis, for which patients turn to doctors?
General symptoms
The symptoms that will be described below exist outside of the localization. These are common symptoms and can exist anywhere. These include pain, movement disorders and sensory disorders. There are also vegetative-trophic disorders, or specific symptoms, for example urinary disorders, but much less frequently. Let's take a closer look at these signs.
Pain: muscular and radicular
Pain can be of two types: radicular and muscular. Radicular pain is associated with compression, or pressure from a protrusion or herniation of the intervertebral disc of the corresponding root at that level. Each nerve root is made up of two parts: sensitive and motor.
Depending on where exactly the herniation is directed and which part of the root has been compressed, there may be sensory or motor disturbances. Sometimes both disorders occur at the same time, expressed to varying degrees. Pain also belongs to sensory disorders, since pain is a particular and specific sensation.
Radicular pain: compression radiculopathy
Radicular pain is familiar to many; it is called "neuralgia". The swollen nerve root reacts violently to any shock and the pain is very sharp, similar to an electric shock. It shoots either in the arm (from the neck) or in the leg (from the lower back). Such a sharp and painful impulse is called lumbago: in the lower back, it is lumbago, in the neck, it is cervicago, a rarer term. Such radicular pain requires forced posture, analgesic or analgesic. Radicular pain occurs immediately when coughing, sneezing, crying, laughing or straining. Any shock to the swollen nerve root causes increased pain.
Muscle pain: myofascial-tonic
But an intervertebral herniation or disc defect may not compress the nerve root, but during movement injure nearby ligaments, fascia and deep back muscles. In this case, the pain will be secondary, aching, permanent, stiffness in the back will occur, and such pain is called myofascial. The source of this pain will no longer be the nervous tissue, but the muscles. A muscle can only respond to any stimulus in one way: contraction. And if the stimulus is prolonged, the muscle contraction will turn into a constant spasm, which will be very painful.
A vicious circle is formed: the spasmodic muscle cannot be well supplied with blood, it becomes deprived of oxygen and it poorly eliminates lactic acid, that is, the product of its own vital activity, in thevenous capillaries. And the buildup of lactic acid again leads to increased pain. It is this type of chronic muscle pain that significantly deteriorates the quality of life and forces the patient to undergo long-term treatment for osteochondrosis, even if it does not prevent him from moving and does not force him tostay in bed.
A characteristic symptom of this secondary myofascial pain will be increased stiffness in the neck, lower back or thoracic spine, the appearance of dense painful muscle bumps - "rolls" next to the spine, that is-i. e. paravertebral. In such patients, back pain intensifies after several hours of "office" work, with prolonged immobility, when the muscles are practically unable to work and are in a state of spasm.
Diagnosis of osteochondrosis
In typical cases, osteochondrosis of the cervical and cervicothoracic spine occurs as described above. Therefore, the main stage of diagnosis has been and remains the identification of the patient's complaints, establishing the presence of concomitant muscle spasms by simple palpation of the muscles along the spine. Is it possible to confirm the diagnosis of osteochondrosis by radiological examination?
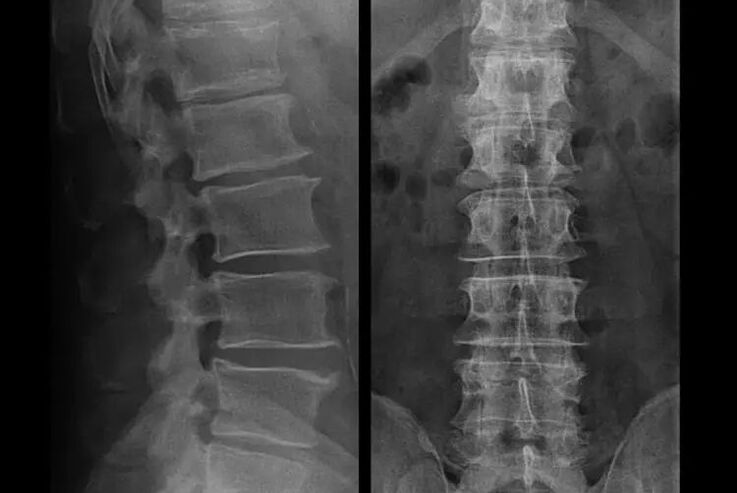
An "X-ray" of the cervical spine, and even with functional tests of flexion and extension, does not show cartilage, because its tissue transmits X-rays. Despite this, based on the location of the vertebrae, wecan draw general conclusions about the height of the intervertebral discs, the general straightening of the physiological curvature of the cou - lordosis, as well as the presence of marginal growths on the vertebrae with prolonged irritation of their surfaces byfragile and dehydrated intervertebral discs. Functional tests can confirm the diagnosis of cervical spine instability.
Since the discs themselves can only be seen using CT or MRI, magnetic resonance and X-ray CT are indicated to clarify the internal structure of cartilage and formations such asprotrusions and hernias. Thus, with the help of these methods, a diagnosis is made accurately and the tomography result is an indication, or even a topical guide, for surgical treatment of a hernia in the neurosurgery department.
It should be added that no other research methods other than imaging, except for MRI or CT scan, can show a hernia. Therefore, if you are given a fashionable "computer diagnosis" of the whole body, if a chiropractor diagnosed you with a hernia by running his fingers along your back, if a hernia was detected based on theacupuncture, a special extrasensory technique, or a session of Thai massage with honey, then you can immediately consider this level of diagnosis completely illiterate. Complications of osteochondrosis caused by protrusion or herniation, compression, muscular, neurovascular, can be treated only by observing the condition of the intervertebral disc at the appropriate level.
Treatment of complications of osteochondrosis
Let us repeat once again that it is impossible to cure osteochondrosis, just like programmed aging and dehydration of the disc. You just can't let things get complicated:
- if there are symptoms of narrowing in the height of the intervertebral discs, then you should move correctly, not gain weight and avoid the appearance of protrusions and muscle pain;
- if you already have a protuberance, then you must be careful not to let it rupture the annulus fibrosus, that is to say not to transform the protuberance into a hernia, and to avoid the appearance of protuberances at several levels;
- if you have a hernia, you need to monitor it dynamically, carry out regular MRI scans, avoid increasing its size or carry out modern minimally invasive surgical treatment, because all conservative methods of treating exacerbation of osteochondrosis, without exception, leave the hernia in place and only eliminate temporary symptoms: inflammation, pain, tightness and muscle spasms.
But with the slightest violation of the diet, lifting heavy objects, hypothermia, injury, gaining weight (in the case of the lower back), the symptoms return again and again. We will describe how you can cope with unpleasant sensations, pain and limited mobility of the back against the background of exacerbation of osteochondrosis and an existing protrusion or hernia, secondary to social tonic syndrome.
What to do during an exacerbation?
Since there was an attack of acute pain (for example, in the lower back), then you should follow the following instructions at the premedical stage:
- completely eliminate physical activity;
- sleep on a hard mattress (orthopedic mattress or hard sofa), eliminating back sagging;
- it is advisable to wear a semi-rigid corset to avoid sudden movements and "deformations";
- You should place a massage pillow with plastic needle applicators on your lower back or use a Lyapko applicator. You should keep it for 30 to 40 minutes, 2 to 3 times a day;
- after that, ointments containing NSAIDs, ointments with bee or snake venom can be rubbed into the lower back;
- after rubbing, on the second day you can wrap the lower back in dry heat, for example, with a belt made of dog hair.
A common mistake is to warm up on the first day. It could be a heating pad, bath procedures. At the same time, the swelling only intensifies, as well as the pain. You can only warm up once the "most painful point" has passed. After that, the heat will encourage the "resorption" of the swelling. This usually happens after 2 to 3 days.
The basis of any treatment is etiotropic therapy (elimination of the cause) and pathogenetic treatment (affecting the mechanisms of the disease). It is accompanied by symptomatic treatment. For vertebrogenic pain (caused by problems in the spine), things go like this:
- In order to reduce swelling of the muscles and spine, a salt-free diet and limitation of the amount of fluid consumed are indicated. You can even give a tablet of a mild potassium-sparing diuretic;
- in the acute phase of lumbar osteochondrosis, short-term treatment can be carried out with intramuscular "injections" of NSAIDs and muscle relaxants: daily, 1. 5 ml intramuscularly for 3 days, 1 ml also intramuscularlyfor 5 days. This will help relieve swelling of nervous tissue, eliminate inflammation and normalize muscle tone;
- in the subacute period, after overcoming the maximum pain, "injections" should no longer be taken and attention should be paid to restorative agents, for example, modern drugs of group "B". They effectively restore impaired sensitivity, reduce numbness and paresthesias.
Physiotherapeutic measures continue, the time has come to resort to exercise therapy for osteochondrosis. Its task is to normalize blood circulation and muscle tone, when swelling and inflammation have already disappeared, but muscle spasms have not yet completely resolved.
Physiotherapy (movement treatment) involves doing therapeutic exercises and swimming. Gymnastics for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is not aimed at the discs at all, but at the surrounding muscles. Its task is to relieve tonic spasms, improve blood flow and normalize venous outflow. This is what leads to a decrease in muscle tone, a reduction in the intensity of pain and stiffness in the back.
In addition to massage, swimming and acupuncture sessions, the purchase of an orthopedic mattress and a special pillow is recommended. A pillow for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine should be made of special "shape memory" material. Its task is to relax the muscles of the neck and suboccipital region, as well as to avoid disruption of night blood flow in the vertebrobasilar region.
Autumn is an important step in the prevention and treatment of home physiotherapy products and devices - from infrared and magnetic devices to the most common needle applicators and ebonite discs, which are a source of weak electric currents duringmassage which have a beneficial effect on the patient.
Exercises for osteochondrosis should be performed after a light general warm-up, on "warmed up muscles". The main therapeutic factor is movement and not the degree of muscle contraction. Therefore, in order to avoid relapses, the use of weights is not allowed; a gymnastics mat and a gymnastics stick are used. With their help, you can effectively restore range of motion.
The application of ointments and the use of the Kuznetsov implicator continues. Swimming, underwater massage, Charcot shower are offered. It is at the stage of the exacerbation that subsides that drugs for magnetotherapy and physiotherapy at home are indicated.
Usually, treatment takes no more than a week, but in some cases osteochondrosis can manifest itself with such dangerous symptoms that surgery may be urgently required.
About Shants Necklace
Initially, during the acute phase, it is necessary to protect the neck from unnecessary movements. The Shants collar is ideal for this. Many people make two mistakes when purchasing this necklace. They do not choose it based on their size, which is why it simply does not perform its function and causes a feeling of discomfort.
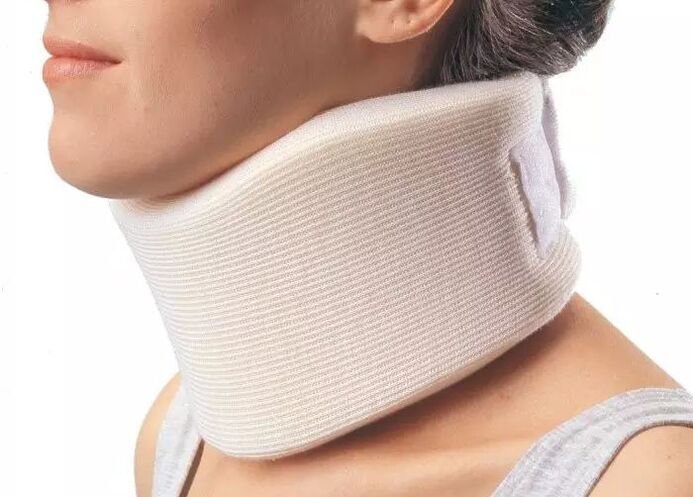
The second common mistake is to wear it for a long time for prophylactic purposes. This leads to weak neck muscles and only causes more problems. For a necklace, there are only two indications under which it can be worn:
- the appearance of sharp pain in the neck, stiffness and pain spreading to the head;
- if you are going to perform physical work in full health, in which there is a risk of "straining" your neck and having aggravation. Examples include repairing a car, when you lie underneath it, or washing windows, when you have to reach out and take uncomfortable positions.
The collar should not be worn for more than 2-3 days, as prolonged wear can cause venous congestion in the neck muscles, when it is time to activate the patient. An analogue of the Shants collar for the lower back is a semi-rigid corset purchased in an orthopedic salon.
Surgical treatment or conservative measures?
It is recommended that each patient, after progression of symptoms, in the presence of complications, undergo an MRI and consult a neurosurgeon. Modern minimally invasive operations make it possible to safely remove quite large hernias, without prolonged hospitalization, without being forced or lying down for several days, without compromising the quality of life, since they are carried out using technologymodern video-endoscopic, radiofrequency, laser or using cold plasma. You can evaporate part of the core and reduce the pressure, reducing the risk of herniation. And you can radically eliminate the defect, that is, get rid of it completely.
There is no need to be afraid of operating on hernias; these are no longer the types of open operations of the 80s-90s of the last century with muscle dissection, blood loss and a long recovery period that follows. Rather, it is a small injection under X-ray control followed by the use of modern technology.
If you prefer a conservative treatment method, without surgery, know that no method will allow you to reduce or eliminate the hernia, no matter what you are promised! Neither an injection of hormones, nor electrophoresis with papain, nor electrical stimulation, nor massage, nor the use of leeches, nor acupuncture can treat a hernia. Creams and balms, physiotherapy and even the introduction of platelet-rich plasma will not help either. And even traction, or traction, therapy, for all its benefits, can only reduce symptoms.
Therefore, the motto of conservative treatment of intervertebral hernias can be the well-known expression "minced meat cannot be turned over. "A hernia can only be eliminated quickly. Prices for modern operations are not that high, because they have to be paid only once. But annual treatment in a sanatorium can ultimately cost 10-20 times more than radical removal of a hernia with the disappearance of pain and restoration of quality of life.
Prevention of osteochondrosis and its complications
Osteochondrosis, including the most complicated ones, the symptoms and treatment of which we discussed above, is for the most part not a disease, but simply a manifestation of inevitable aging and premature "shrinking" of the intervertebral discs. Osteochondrosis needs few things to never bother us:
- avoid hypothermia, especially in autumn and spring, and falls in winter;
- do not lift weights and carry loads only with your back straight, in a backpack;
- drink more clean water;
- do not gain weight, your weight must correspond to your height;
- treat flat feet, if present;
- do physical exercises regularly;
- practice types of exercises that reduce the load on the back (swimming);
- give up bad habits;
- alternate mental stress and physical activity. After every hour and a half of mental work, it is recommended to change the type of activity to physical work;
- You can regularly do at least one x-ray of the lumbar spine in two projections, or an MRI, to find out if the hernia, if present, is progressing;
By following these simple recommendations, you can keep your back healthy and mobile for a lifetime.























